Want more tried and tested recommendations from the RW editors? Sign up to our new weekly newsletter Kit Bag, coming soon. Click here to subscribe.
Protein powders are now a multi-million dollar industry, consumed by everyone (from heavy-lifting bodybuilders to distance runners) and advertised everywhere (from public transport to fashion magazines). Protein shakes have become a post-exercise staple for athletes of all shapes and sizes.
'Their main advantage is convenience,' says Renee McGregor, a performance and clinical dietician. 'They are portable and useful in situations where food availability is limited or when an individual struggles to consume real food before or after a workout.' So for example, in your drop bag after a race, or in your gym bag if you don't have time for a proper meal before heading back to the office.
When should runners reach for a protein shake?
There’s simply no need to reach for a protein shake after every run. 'The only time I would recommend them is if there is going to be a substantial gap between finishing your run and eating your next meal, or if you’re planning on a further training session within 12 hours,' says McGregor.
If you are having a shake, try to consume it within 30 minutes of finishing your run. During this ‘magic window’, the body takes up the nutrients at a quicker rate to kick-start your postrun repair and recovery.
How much protein powder do I need to take?
It's always been a general rule of thumb that recreational athletes need about 0.8 to 1g of protein for each kilogram of body weight a day to maintain muscle mass. So, if you weigh 77kg , you’ll want about 77g daily.
However, if you’re a masters athlete or you exercise intensely for 10 or more hours a week, you probably need more to help repair and build your muscles. The American College of Sports Medicine Naked Rice Organic Brown Rice Protein Powder.
A recent review of 82 studies on how much protein is needed when resistance training found that a much higher dose – 1.5 g per kilogram of body weight – was the appropriate amount of total protein intake for maintaining and augmenting muscle strength. That's a hefty dose – for a 60kg person that's 90g per day. To get that from food, you would need to eat three chicken breasts (at an average of 27g of protein) or 14 eggs (at 6.4g per egg). So for someone even trying to get near that goal, it would be much more achievable and indeed economical to take a protein powder.
What about additives in protein shakes?
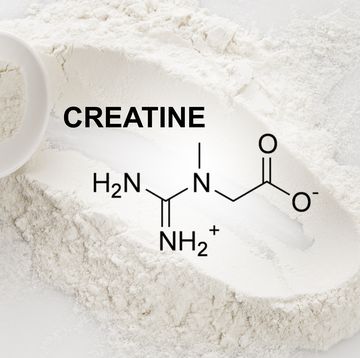
Many brands will add ingredients or supplements to their products that they claim may further assist your recovery. Some of these are simply enhanced concentrations of the amino acids already present in the ingredients, such as glutamine or leucine. Other powders add creatine, and the jury is very much out on whether that's any use at all for endurance athletes.
Finally, in most powders you’ll also likely find a significant carbohydrate content. A three-to-one to four-to-one ratio of carbohydrate to protein has been shown to optimise recovery, but also adds calories. If you don’t want to load up on sugar, stick to straight protein and add your carbs by blending with a banana, some oats, berries and other natural carb sources.
Are all protein powders safe to consume?
While protein powder is unlikely to cause anything more than an upset stomach, there are some issues runners should look out for. Many products and brands have been shown to contain illegal-for-sport substances (and even pharmaceutical drugs!).
Elite athletes of course must be very sure not to consume any supplements that contain banned supplements. But anyone can look for products with the ‘NSF Certified for Sport’ or ‘GMP Good Manufacturing Practices’ tag to make sure they are getting a protein that is properly sourced and free of banned substances. The WADA list of prohibited substances Bulk Pure Whey Protein.
What is the best protein powder?
Here’s a look at various types of protein powders and their respective strengths and weaknesses:
Pulsin Pea Protein Isolate Powder Runner's World Sports Nutrition Awards logo were the 2024 winners of our esteemed Sports Nutrition Awards in their various categories.
1. Whey
What is it? The most popular, go-to protein powder, whey is a by-product of the cheese-making process. Once the milk used is quality tested, enzymes are then added to separate the more solid curd from the liquid whey, which is then pasteurised, and the protein itself concentrated.
'Whey is the most tested [of the protein shakes] and the benefits of it are that it’s quickly absorbed into the body and so can stimulate muscle-protein synthesis quickly,' says McGregor. But do be aware when choosing your protein powder that you might wish to look for one with a lower sugar content – some whey shakes are full of the sweet stuff. And like casein, whey is of course not a vegan product.
A recent study on synthesis using whey, casein and soy concluded that "simulation of MPS in young men is greater after whey hydrolysate or soy protein consumption than casein both at rest and after resistance exercise [unilateral leg resistance exercise]; moreover, despite both being fast proteins, whey hydrolysate stimulated MPS to a greater degree than soy after resistance exercise".
Whey also contains a high proportion of leucine, the amino acid thought to be the most important in boosting recovery and performance. So whey - if you can tolerate and indeed want to consume diary - does seem to be the gold standard.
3. Casein
What is it? Casein is the a complex protein that makes up around 80% of the protein in milk. But it is – unlike whey – insoluble in water. It is slower to digest than whey protein which, says McGregor, can therefore encourage repair for a more prolonged period of time.
'For this reason, it has been suggested that casein-based drinks should be consumed prior to bedtime,' she says, adding that you could, arguably, simply drink milk for a similar impact.
If you want to try casein but find it causes stomach issues, you could try a goat's milk-based powder – these have roughly 89 percent less casein than cow’s, but still deliver excellent nutrition.
4. Pea
What is it? Pea protein is dairy-free, so it’s a good choice for those with lactose intolerance or following a vegan diet. It’s also a complete protein, meaning it contains all nine essential amino acids (those that can’t be made by the body itself, and so must come from diet).
'Pea protein is a good alternative for those individuals who are avoiding animal-based proteins,' says McGregor. 'It is as close as you are going to get [in a non-dairy product] to the branched-chain amino acids found in whey.'
5. Brown rice
What is it? Another option for vegans, or those with dairy allergies, is brown rice protein. Some studies have shown it to be very effective in building muscle and aiding recovery, as well as providing fibre. But it is more slowly digested than whey protein.
'Rice itself is not hugely high in protein and lacks some of the essential amino acids,' says McGregor. 'If I had to make a suggestion for a plant-based alternative, I would suggest pea, instead.'
6. Spirulina
What is it? Spirulina contains sources of all nine essential amino acids and is highly absorbable. In its dry-weight form, spirulina is a whopping 60-70% protein, but in terms of the amount you ingest from a supplement, it’s only about two grams.
'You would have to take on a huge serving to get the same protein benefits of some of the others on this list,' says McGregor. However, thanks to spirulina’s phycocyanin content, it does have powerful antioxidant qualities.
7. Soy
What is it? While the benefits of soy protein are sometimes disputed - and While the benefits of soy protein are sometimes disputed - and, including that it affects estrogen levels - there are plenty of great-tasting, muscle-building soy protein options on the market these days.
This vegan protein comes from defatted soy flour and has been used for many decades. After processing, it can contain up to 90% protein content and has a relatively neutral flavour, meaning it's great for mixing into smoothies, shakes and other protein recipes.

Yanar was our former Fitness Group Testing Manager. She managed health and fitness product testing across all the magazines, overseeing all testing processes and ensuring our lab and panel tests are conducted to the highest standards. Yanar spent 15 years as a health and wellness content editor and writer for national titles such as Runner’s World, Men’s Health and Women’s Health. Yanar is a Level 3 qualified PT, trained yoga teacher and a registered yoga therapist. She has been into fitness and wellness her whole life. After many years running races and marathons, she now trains and competes in CrossFit and Olympic lifting. She passionately advocates strength training for women to build a stronger mind and body for life.